The International Olive Council (IOC) is the only international organisation dedicated to olive oil and table olives. It is based in Madrid, where it was created in 1959 under the auspices of the United Nations. The Council contributes decisively to the responsible and sustainable development of the olive grove defending olive cultivation and promoting its produce worldwide and constitutes a global forum where the policies to be adopted are debated and the challenges to be faced by the sector are discussed.
The International Agreement on Olive Oil and Table Olives, 2015 (The “Agreement”) is the legal instrument underpinning the existence of the International Olive Council (IOC).
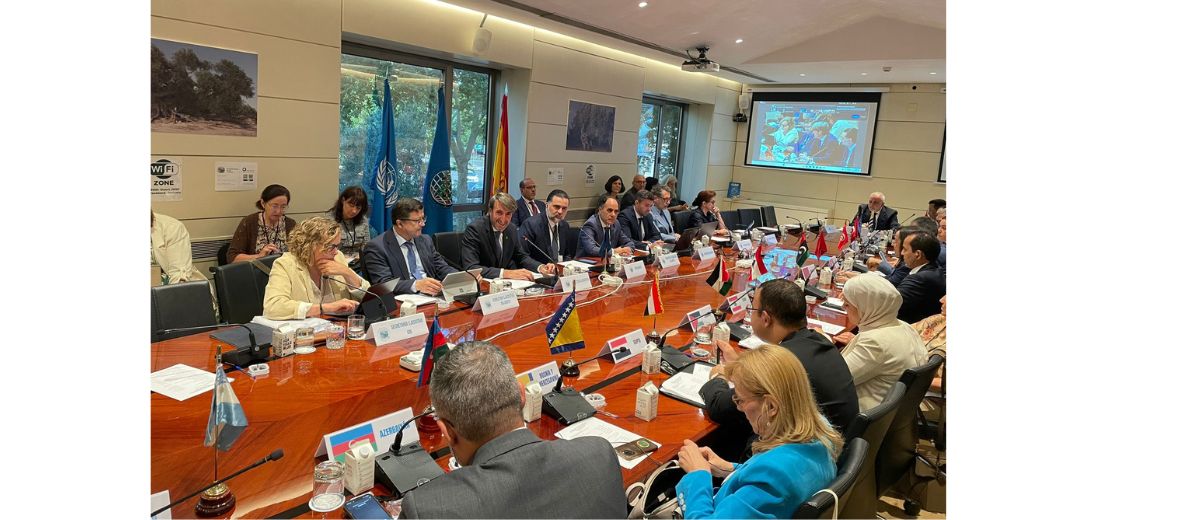
The following (1) are ParTies To The agreement and Members of the Council: Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Egypt, The European Union (with its 28 Member States1 ), Georgia, the Islamic Republic of Iran, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Libya, Montenegro, Morocco, the State of Palestine, Tunisia, Turkey and Uruguay. The current membership of the organisation (2) accounts for around 94,2% of the olive oil and 90.4% and table olives produced in the world. Additionally, the Agreement covers other highly important topics, such as environmental and ecological issues and the relationship between the olive sector and business.
1 Member States of the European Union: Austria, belgium, bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain and Sweden. To date also United Kingdom.
2 According to the definitive data approved in the 2016/17 olive crop year: Olive oil 92.6%, Table olives 86.7%. According to the last data not approved and that may change olive crop year 2017/18: Olive oil 95,0% and Table olives 91,0%. Olive Oil 94.2% and Table olives 90.4 are expected for the 2018/19 olive crop year.
The measures incorporated into the Agreement are focused on the following fundamental lines of action: promotion of olive products, dissemination of information and the olive economy; olive growing, olive oil techonology and technical cooperation; standarisation and research.
Environmental and ecological aspects: According to the Agreement, members shall give due consideration to the improvement of practices at all stages of olive and olive oil production in order to guarantee the development of sustainable olive growing and undertake to implement such action as may be deemed necessary by the Council of Members to improve or solve any problems encountered in this sphere.
The IOC has a close working relationship with business through its Advisory Committee on Olive Oil and Table Olives, which was made to facilitate dialogue between key players in the olive sector and the Council. The IOC recently decided to intensify its interaction with this Committee and involve it more in its activity.